In any scaffolding system, the working platform is where productivity and safety come together. While standards, ledgers, and braces provide the structural framework, it is the decking that directly supports workers, tools, and materials. Among the various platform solutions available, scaffolding hook planks play a particularly important role. From a buyer's and end user's perspective, understanding how hook planks are used in scaffolding systems helps ensure safer installations, smoother operations, and better long-term value.
What Is a Scaffolding Hook Plank?
A scaffolding hook plank is a prefabricated platform board equipped with integrated metal hooks at one or both ends. These hooks are designed to sit securely over transoms, ledgers, or designated support members within a scaffolding system. Once positioned, the plank is mechanically restrained by its own geometry, minimizing the risk of sliding or uplift.
Hook planks are commonly manufactured from steel, aluminum, or timber, with steel and aluminum being the most widely used in modern modular scaffolding systems such as Ringlock, Cuplock, Kwikstage, and frame scaffolding.
Installation and Positioning in the Scaffolding System
The use of hook planks follows a simple but reliable installation process:
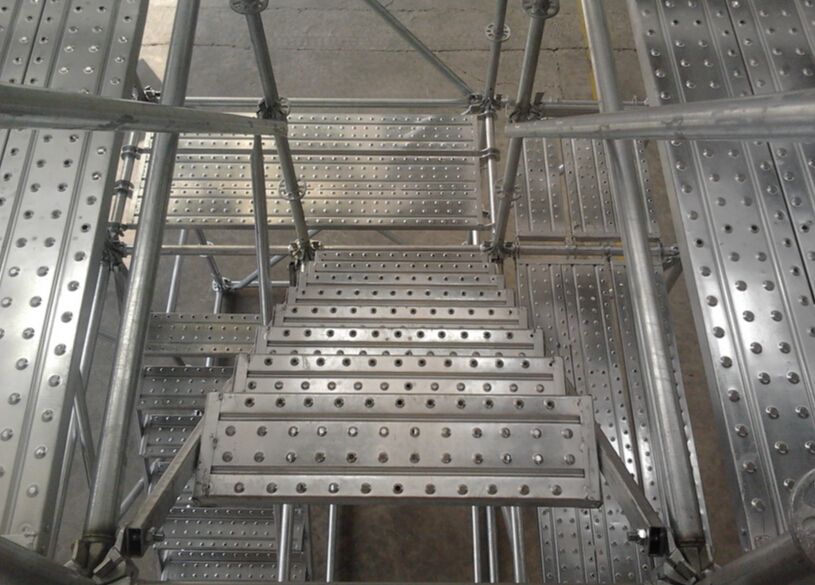

Alignment with Structural Members
The installer lifts the hook plank and aligns it with the transoms or ledgers that define the working level.
Engaging the Hooks
The hooks are lowered onto the supporting members, allowing gravity to seat the plank firmly in place.
Final Stability Check
The plank is checked for proper seating, levelness, and secure engagement before use.
This process does not usually require additional clips or fasteners, which makes hook planks especially attractive on projects where speed and repetition are important.
Typical Applications of Hook Planks
Scaffolding hook planks are used in a wide range of site conditions and applications:
Primary Working Platforms
They form the main walking and working surface for trades such as bricklaying, plastering, cladding installation, and painting.
Access Walkways
Hook planks are often installed as internal walkways between bays, allowing workers to move safely and efficiently along the scaffold.
Edge and Cantilevered Platforms
Because the hooks help prevent uplift and movement, hook planks are well suited for edge zones or return platforms where standard boards may be less stable.
Temporary Bridging Decks
On some sites, hook planks are used to bridge short gaps or obstacles, provided load ratings are respected.
Advantages Over Traditional Loose Boards
From both safety and operational standpoints, hook planks offer several clear advantages when compared to traditional loose-laid boards:
Enhanced Safety
The hooked connection significantly reduces the risk of planks slipping, lifting in high winds, or being accidentally displaced during work.
Faster Assembly and Dismantling
With no need for nails, ties, or separate retaining clips, hook planks can be installed and removed quickly, reducing labor time.
Consistent Platform Quality
Factory-manufactured hook planks provide uniform length, width, and hook positioning, helping maintain consistent bay spacing and compliant platform widths.
Improved Site Organization
Standardized planks simplify inventory management and reduce the likelihood of incompatible components being mixed on site.
Compatibility With Different Scaffolding Systems
Hook planks are not universally interchangeable; they are designed to match specific system dimensions and profiles:
In Ringlock systems, hook planks typically rest on system transoms connected at the rosette nodes.
In Cuplock systems, the hooks engage with horizontal members locked into the cup joints.
In Kwikstage systems, hook profiles are shaped to suit the ledger section and standard bay widths.
For buyers, this means system compatibility must be confirmed before purchase to ensure safe seating and proper load transfer.
Load Capacity and Safety Considerations
Each hook plank is designed with a defined safe working load (SWL), which includes the weight of workers, tools, and materials. Proper use requires:
Even distribution of loads across multiple planks.
Avoiding point loads that exceed design assumptions.
Regular inspection of hooks, welds, and plank surfaces for damage or corrosion.
Most reputable manufacturers mark hook planks with load ratings and relevant standards, making compliance easier to manage on site.
Inspection, Maintenance, and Service Life
Routine inspection is essential to ensure continued safe use. Site supervisors should check for bent hooks, cracked welds, excessive wear, and surface damage. Galvanized steel planks generally offer the longest service life, while aluminum planks provide advantages in weight and handling.
Proper storage, avoiding impact damage, and removing defective planks from service promptly all contribute to lower long-term ownership costs.
Conclusion
Scaffolding hook planks are a practical and safety-focused solution for creating stable working platforms within modern scaffolding systems. By securely engaging with the scaffold structure, they reduce movement risks, speed up installation, and support consistent site standards. For contractors and buyers alike, understanding how hook planks are used—and selecting high-quality, system-compatible products—is a key step toward safer, more efficient scaffolding operations.